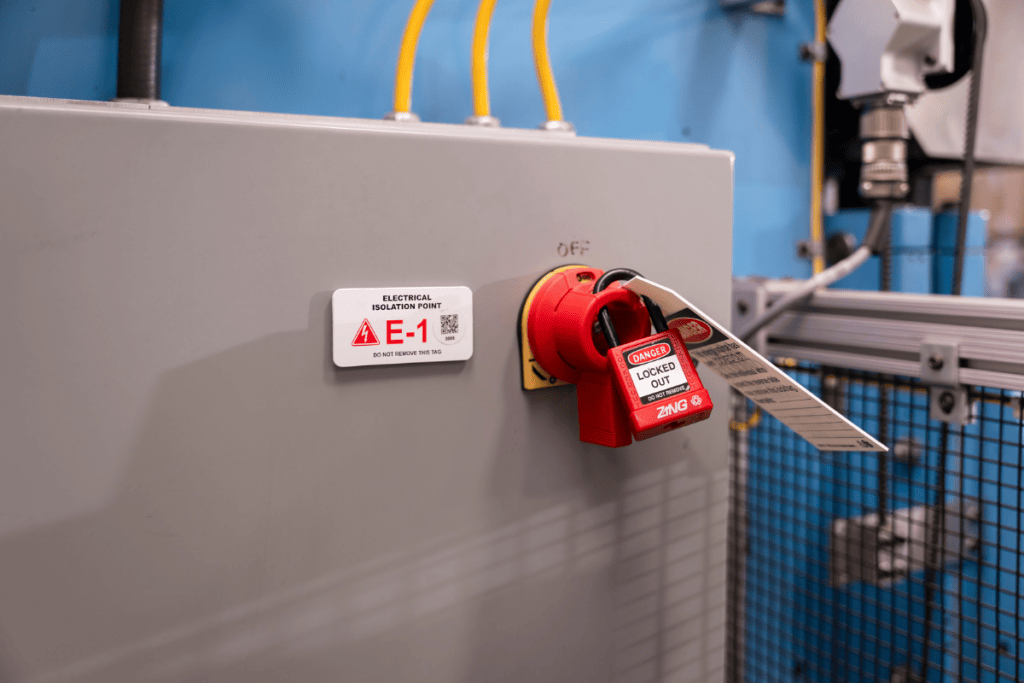
Lockout tagout (LOTO) procedures are essential for ensuring the safety of workers during the maintenance and servicing of machinery and equipment. By controlling hazardous energy, these procedures prevent accidental energization, which can lead to serious injuries or fatalities. This article outlines and explains the key parts of effective lockout tagout procedures to help organizations create and maintain a safe working environment.
10 Steps of Lockout Tagout Procedures
Lockout tagout procedures can be broken down into 10 simple steps:
- Prep for Shutdown
- Equipment Shutdown
- Isolation of Energy Sources
- Lockout Tagout Device Application
- Dissipation of Residual or Stored Energy
- Verification of Isolation
- Performing Maintenance or Servicing
- Release from Lockout Tagout
- Equipment Restart
- Documentation and Recordkeeping
Each one of these steps plays a crucial part in maintaining safety and is essential for the proper control of hazardous energy. Therefore, steps should not be skipped, ignored, or partially completed. Missed steps, whether on purpose or accident, can dramatically increase the likelihood of a fatal worker injury or accident. Because of this, all individuals participating in lockout tagout procedures are encouraged to be familiar with and follow these 10 steps.

Scott Stone Performing Lockout Tagout Procedures on a Tablet
Quick Overview of Each Step
Now, let’s break down each of the 10 essential steps of lockout tagout procedures. To do this, the following section will dive into the significance of each step and how workers are expected to complete it.
Step 1: Preparation for Shutdown:
- Objective: Preparing for shutdown is the initial step in lockout/tagout procedures, where you systematically plan for the safe deactivation of equipment.
- How to: During this phase, you identify all sources of energy connected to the machinery or system, review equipment manuals, and determine the correct procedures for shutting down the system. This step involves notifying affected personnel, assessing potential hazards, and ensuring you have the necessary tools and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the process.
Proper preparation is crucial to ensure a smooth, safe, and effective shutdown.
Step 2: Equipment Shutdown:
- Objective: Equipment shutdown is the second step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves the actual process of turning off the machinery or system.
- How to: During this phase, you follow the specific shutdown procedures identified in the preparation step to safely stop the equipment. This often includes turning off power sources, closing valves, or disengaging moving parts. It’s essential to ensure that the equipment is fully powered down and that all energy sources are properly isolated to prevent any unexpected activation.
This step is crucial for creating a safe environment for maintenance or repair work, minimizing the risk of accidental injury.
Step 3: Isolation of Energy Sources:
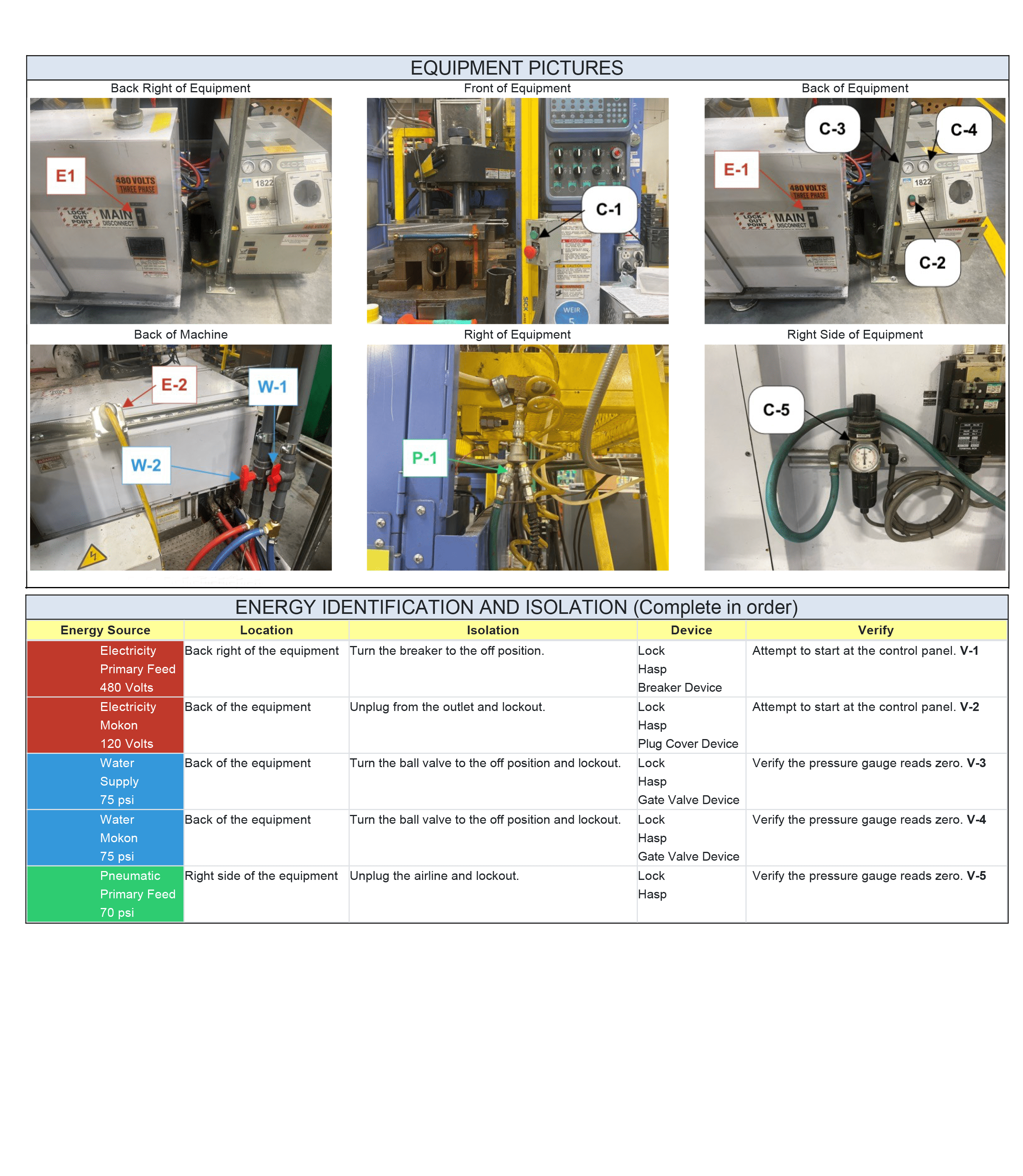
- Objective: Isolation of energy sources is the third step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves disconnecting or isolating all sources of energy to ensure that the equipment remains in a de-energized state.
- How to: During this step, you ensure that the equipment is cut off from all energy sources. This may include turning off circuit breakers, closing valves, or disconnecting mechanical linkages.
Proper isolation is crucial to prevent the accidental release of energy, which helps ensure the safety of maintenance personnel and protects the equipment from damage.
Step 4: Lockout/Tagout Device Application:
- Objective: Lockout/Tagout device application is the fourth step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves physically applying lockout and tagout devices to energy-isolating mechanisms.
- How to: In this step, you attach lockout devices, such as padlocks or lockout hasps, to circuit breakers, valve handles, or other isolation points to prevent their operation. You also place tags on these devices to clearly communicate that maintenance is being performed and that the equipment should not be operated. During this step, ensure that each lock and tag is applied by the authorized employee who is performing the maintenance.
This step ensures that the energy sources remain securely isolated and that all personnel are aware of the ongoing maintenance, thereby preventing accidental re-energization and ensuring a safe working environment.
Step 5: Dissipation of Residual or Stored Energy:
- Objective: Dissipation of stored energy is the fifth step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves safely releasing or neutralizing any stored or residual energy that could pose a risk.
- How to: During this step, relieve, disconnect, or restrain any residual energy sources (such as hydraulic or pneumatic pressure, electrical capacitors, or spring tension). You may take actions such as venting or draining fluids, releasing tension from springs, and ensuring that all stored energy is fully dissipated or securely contained.
Proper dissipation is crucial to eliminate any potential hazards and to ensure that the equipment is completely safe for maintenance or repair work.
Step 6: Verification of Isolation:
- Objective: Verification of isolation is the sixth step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves confirming that the equipment is properly isolated and de-energized before beginning maintenance work.
- How to: During this step, you check and test the equipment to ensure that all energy sources have been effectively locked out and that no residual energy remains. This may include attempting to operate the equipment controls, measuring electrical voltage, or checking pressure gauges to verify that the equipment is in a zero-energy state. Along with this, double-check that all lockout and tagout devices are securely in place.
Proper verification ensures that all safety measures are in place and confirms that the environment is safe for personnel to proceed with maintenance or repairs.
Step 7: Performing Maintenance or Servicing:
- Objective: Performing servicing and maintenance is the seventh step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves carrying out the necessary repair or maintenance tasks on the equipment.
- How to: Once verification of isolation is complete and it’s confirmed that the equipment is in a safe, de-energized state, you can proceed with the actual servicing activities. This step includes tasks such as inspecting, repairing, or replacing components according to established procedures. During this phase, it’s crucial to follow safety protocols, use appropriate tools and personal protective equipment (PPE), and adhere to any specific maintenance guidelines to ensure both personal safety and effective repair work.
All the previous steps help make this step possible in a safe working environment.
Step 8: Releasing from Lockout/Tagout:
- Objective: Release from lockout/tagout is the eighth step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves carefully removing lockout and tagout devices once maintenance or servicing is complete.
- How to: Before anything else, notify all affected employees that the lockout tagout devices will soon be removed. Then, follow a systematic process to ensure that all tools and equipment have been removed from the work area and that all safety checks are completed. This includes confirming that all guards and safety devices are reinstalled and functioning correctly. Once that is complete, remove all lockout and tagout devices in reverse order of application (by the same authorized employee(s) who put it on initially).
This step is critical for ensuring that the equipment is fully restored to its operational state and that all safety protocols are adhered to before allowing it to be used again.
Step 9: Equipment Restart:
- Objective: Equipment restart is the ninth step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves reactivating the equipment following maintenance or repair work.
- How to: In this phase, you carefully follow the established startup procedures to ensure that the equipment is returned to normal operation safely. This includes removing any barriers or obstructions, re-engaging energy sources, and conducting a thorough check to confirm that all systems are functioning correctly. It’s important to monitor the equipment closely during the initial restart to detect any issues promptly and ensure that everything operates as expected.
This step marks the transition from maintenance to normal operation, ensuring that the equipment is safe and ready for use.
Step 10: Documentation and Recordkeeping:
- Objective: Documentation and recordkeeping is the final step in lockout/tagout procedures and involves accurately recording all activities related to the lockout/tagout process to promote accountability and regulatory compliance.
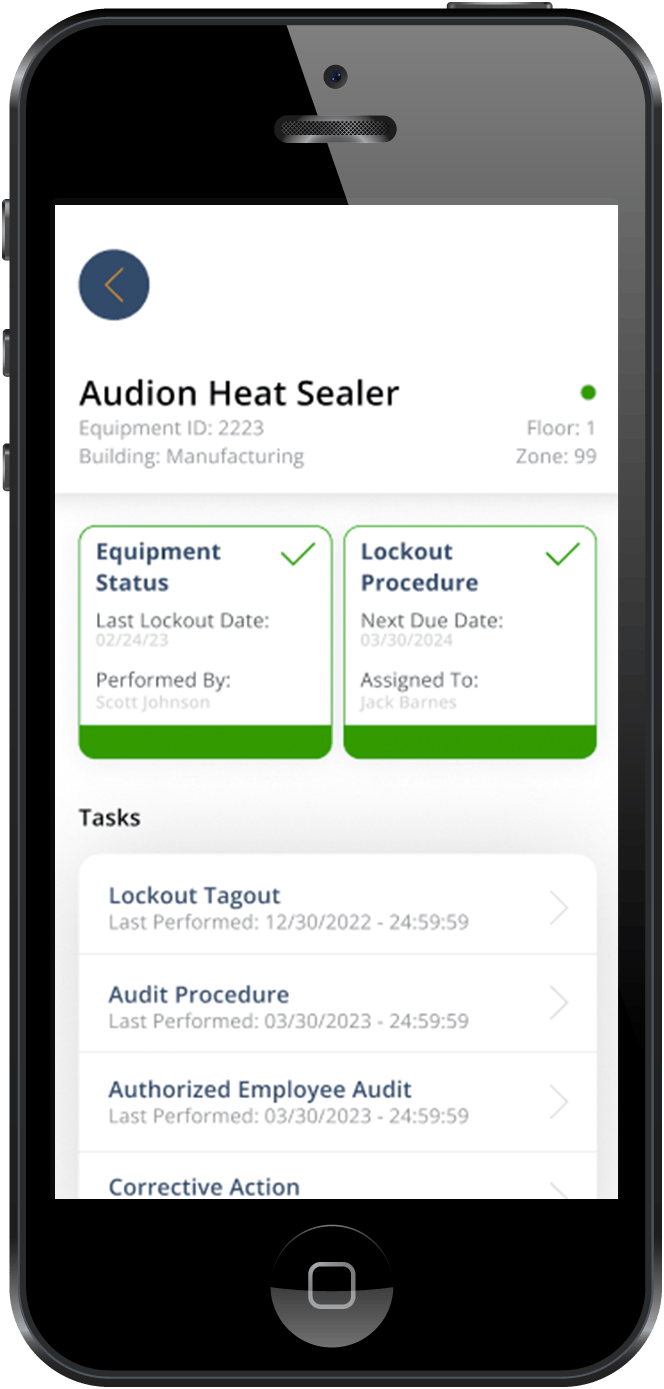
- How to: During or after lockout tagout procedures, document the event with information including the date, time, equipment involved, personnel responsible, and any issues needing attention. This documentation can either be recorded manually on paper documents or digitally in software. Records should include a history of all training sessions, inspections, and any incidents related to LOTO procedures. Proper recordkeeping ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, facilitates future safety audits, and provides a clear history of maintenance activities.
This step helps in tracking the effectiveness of safety protocols and can be valuable for improving lockout/tagout procedures, maintaining a consistent inspection schedule, and providing documentation during audits.
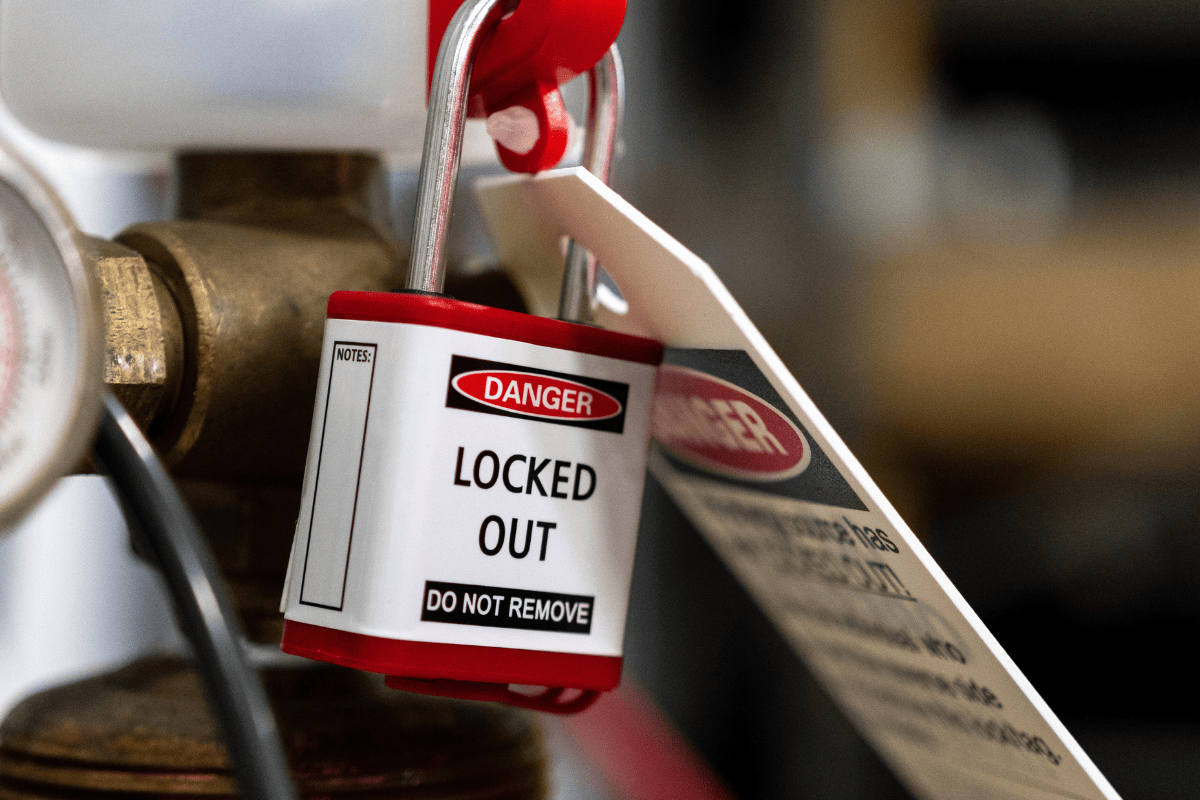
Lockout Tagout Procedures – Lock and Tag On a Machine
Performing Lockout Tagout Procedures With Software
While there are many who still use traditional methods to perform lockout tagout procedures, there is also a growing interest in utilizing software to simplify and streamline safety measures in the workplace. That is why Smart Safety Pro was created. It is a software solution designed to make safety in the workplace easier, particularly for lockout tagout.
Here are some of the top benefits available to those who use Smart Safety Pro software for their lockout tagout procedures:
- Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency: With software, workers can ditch the traditional approach to manual documentation and reporting. Instead of handling loose papers, workers can digitally input their procedures and reports, which helps with report consistency and overall accuracy. The risk of human error is significantly reduced and documentation is simplified.
- Improved Compliance: Smart Safety Pro’s software offers a systematized way of conducting and recording lockout tagout procedures. Having this structure promotes compliance with regulatory requirements and company policies. Additionally, software can be used to generate detailed reports and records, which are essential for audits, inspections, and regulatory reviews.
- Real-Time Updates and Communication: Because Smart Safety Pro software works offline, workers can input data and update it anytime, anywhere. This allows for real-time updates and access to procedures, ensuring that maintenance personnel always have the most current information at their fingertips. Current flow of information increases team communication and collaboration.
- Enhanced Training and Guidance: Those who choose to invest in lockout tagout software with us have the option to receive training, either in person or remote. This allows new users to get hands-on experience with the guided assistance of a specialist. Along with the initial training, users can access an online knowledge base when they need a refresher on certain aspects of using the software. This supports better training and onboarding of new employees.
- Data Analytics and Insights: Our software stores all lockout/tagout program data, making it easy for that data to be analyzed for trends, performance, and areas of improvement. This data-driven approach helps in optimizing procedures and enhancing safety measures.
- Increased Efficiency: With our software, users can build lockout tagout procedures in minutes! Not only that, but the ease of digital reporting significantly cuts down the time needed for performing procedures. These together help increase operational efficiency.
- Centralized Management: Software provides a centralized platform for managing all lockout/tagout activities, making it easier to oversee and coordinate procedures across multiple sites or facilities from a single point of access.
Overall, integrating software into lockout/tagout procedures enhances safety, compliance, and efficiency, leading to a more organized and effective safety management system.
Try Smart Safety Pro’s LOTO Software
Want to learn more about what Smart Safety Pro is and how it can help with lockout tagout procedures? If so, connect with our team by requesting a demo!
Our team of specialists are happy to set up a meeting to help you determine if Smart Safety Pro software is right for your company’s needs. We believe in the power of our product to change the way safety is approached in the workplace and want to answer any questions you have.
The previous section highlighted many benefits of our software, but here are some top-loved features from our customers:
- LOTO procedure builder – Highly customizable!
- Centralized data platform: All your info in one place.
- User-friendly interface: Intuitive user experiences.
- Organized digital reports and data: Paper free!
- On-the-go reporting: No wifi needed.
We have a multitude of solution offerings, and hope that you will give us the chance to show just what our lockout tagout software can do!
Conclusion
Effective lockout tagout procedures are vital for protecting workers from hazardous energy during maintenance and servicing activities. To complete lockout tagout procedures properly there are 10 essential steps that workers need to be familiar with. Each step plays a vital role in the overall safety of workers and should be taken seriously. Workers who familiarize themselves with these 10 steps will be better equipped to perform their duties, protect themselves, and promote safety for others. By understanding and implementing the lockout tagout steps, organizations can create a safer work environment, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, and prevent workplace accidents and injuries. Along with these 10 steps, another aid for completing lockout tagout procedures is LOTO software. Smart Safety Pro offers a valuable product that can provide many features and benefits to enhance lockout tagout programs and procedures. Learn more about Smart Safety Pro software here.