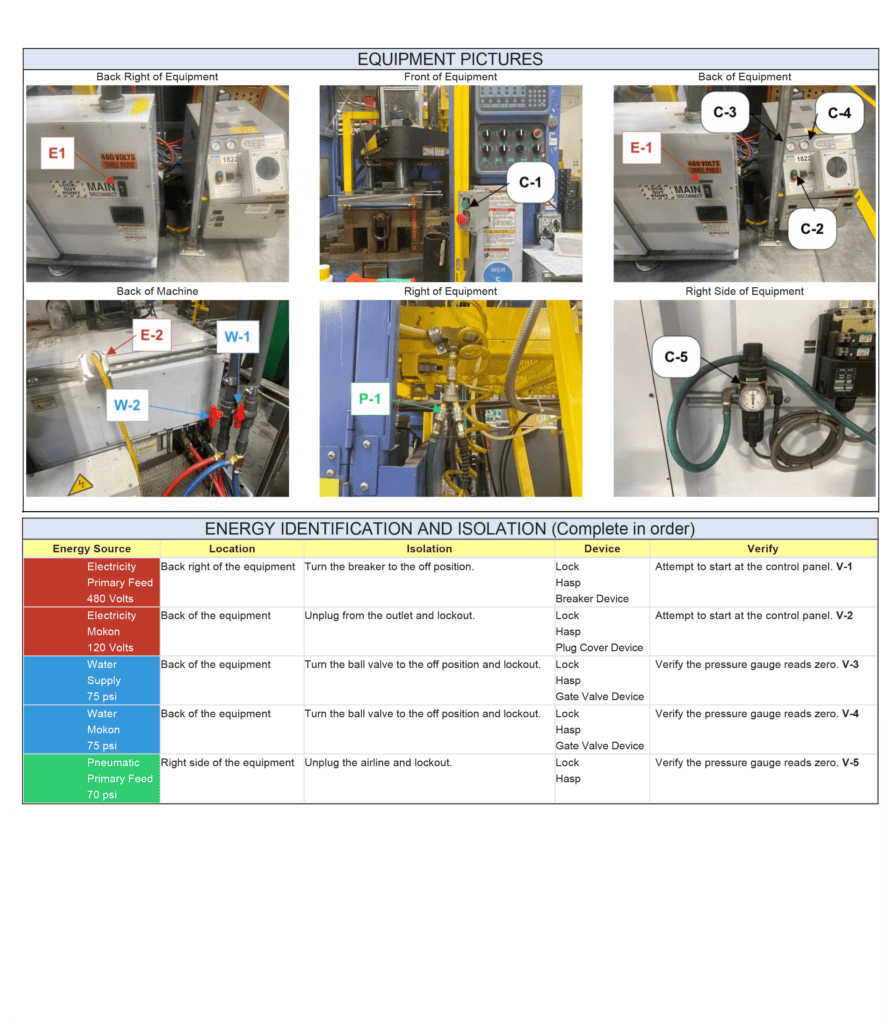
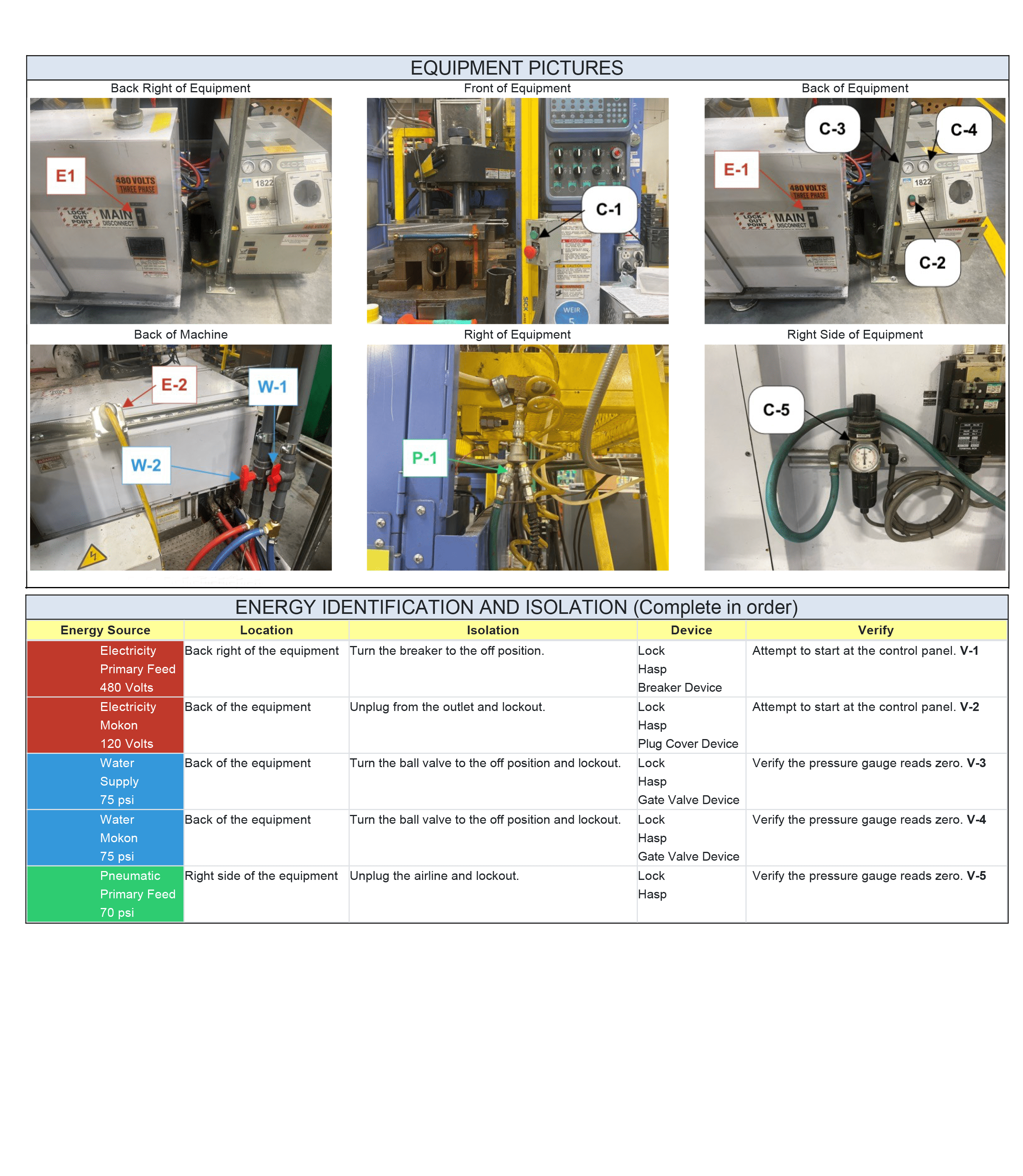
In the dynamic world of industries and workplaces, safety is a non-negotiable priority. Amidst the hum of machinery and the intricacies of modern technology, one crucial safety protocol takes center stage – the Lockout Tagout (LOTO) procedure. This article aims to unravel the intricacies of what a Lockout Tagout procedure entails, exploring its definition, key components, and the indispensable role it plays in preserving lives and safeguarding equipment.
Defining a Lockout Tagout Procedure
The Lockout Tagout procedure, often abbreviated as LOTO, is a safety procedure employed in industrial settings to ensure the complete isolation of energy sources from machinery or equipment during maintenance, repair, or servicing activities. The goal is simple yet profound – to prevent accidental energization or startup of machinery, which could pose serious risks to the safety of personnel involved.
Key Components of Lockout Tagout Procedure
1. Lockout
The central aspect of the lockout tagout procedure involves physically locking the energy-isolating devices to prevent the release of hazardous energy. These devices may include circuit breakers, valves, switches, or any other mechanism controlling the flow of energy to the equipment.
Lockout devices typically come in the form of padlocks or similar mechanisms. These locks serve as a visible indication that the equipment is in a state of isolation and should not be operated.
2. Tagout
Complementing the lockout element of this procedure is the tagout component. Tags, often brightly colored and prominently displayed, are fastened to the locked-out energy isolating devices.
Tags provide essential information such as the reason for the lockout, the individual responsible for the lockout, and the expected duration of the lock out. This information ensures clarity and aids in communication among workers involved in the maintenance activity.
3. Energy Isolation Devices
These are the physical components, such as switches or valves, that control the flow of energy to the equipment. Energy isolation devices must be capable of being locked to ensure the effectiveness of the lock out tag out procedure.
Identifying and isolating all potential energy sources associated with the machinery is a critical step in the Lockout Tagout process.
The Purpose and Significance of LOTO Procedure
- Worker Safety
- At the forefront of the purpose of a Lockout Tagout procedure is the protection of workers. By ensuring that equipment is properly shut down and isolated, LOTO prevents accidental energization, significantly reducing the risk of injuries, electrocutions, or fatalities during maintenance or repair tasks.
- Lockout tagout procedures foster a safety-first culture, emphasizing the well-being of personnel engaged in potentially hazardous activities.
- Accident Prevention
- LOTO is a potent tool in preventing accidents caused by unexpected equipment activation. Accidents, such as amputations, crush injuries, or electrocutions, often result from machinery starting up unexpectedly during maintenance or repair.
- The use of locks and tags acts as a visual and physical barrier, serving as a warning to other workers and preventing them from inadvertently re-energizing the equipment.
- Legal Compliance
- Beyond being a best practice, Lockout Tagout procedures are often a legal requirement. Regulatory bodies, including the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, mandate the implementation of LOTO procedures in workplaces where the release of hazardous energy is a potential hazard.
- Adhering to these regulations not only ensures the safety of workers but also shields organizations from legal ramifications and financial liabilities.
- Integrity
- Lock out Tag out procedures extend beyond protecting human lives; they also safeguard the integrity of equipment. Sudden energization during maintenance can cause damage to sensitive components, leading to costly repairs and downtime.
- By enforcing LOTO protocols, organizations ensure that maintenance tasks are carried out in a controlled environment, minimizing the risk of damage to equipment and maximizing its operational lifespan.
- Operational Efficiency
- Contrary to a common misconception, integrating Lockout Tagout procedures does not decrease overall operational efficiency. In fact, this form of routine maintenance actually enhances productivity, by promoting a longer life span of machinery. LOTO provides a structured and standardized approach to isolating and de-energizing equipment, streamlining the maintenance processes.
- Workers can perform their tasks confidently, knowing that the equipment is safely shut down, resulting in faster and more efficient maintenance procedures.
- Risk Management and Hazard Identification
- LOTO procedures necessitate a comprehensive understanding of the energy sources associated with each piece of equipment. This requirement encourages organizations to conduct thorough risk assessments and hazard identifications.
- By scrutinizing potential sources of hazardous energy, companies can develop effective strategies to mitigate risks, enhancing workplace safety beyond the confines of Lockout Tagout procedures.
- Worker Empowerment and Accountability
- Implementing Lockout Tagout procedures foster a culture of safety and responsibility among workers. Training programs associated with LOTO educate employees about the potential dangers of hazardous energy and the critical role they play in ensuring their safety.
- Empowering workers with the knowledge and tools to implement Lockout Tagout procedures creates a more accountable and safety-conscious workforce.
The Lockout -Tagout Procedure in Action
1. Preparation
Before initiating the Lock out Tag out procedure, thorough preparation is essential. This involves developing a comprehensive plan outlining all energy sources associated with the equipment, isolation points, and specific steps for shutting down and securing the equipment.
2. Notification
All affected employees must be notified of the impending lockout. This ensures that everyone is aware of the maintenance activities, reducing the risk of inadvertent attempts to start the equipment during the lockout period. Communication is paramount.
3. Equipment Shutdown
Once everyone is informed and prepared, the equipment is shut down using its normal stopping procedure. This step ensures that the machinery is in a safe state before proceeding with the lock out.
4. Energy Isolation
Identifying and turning off energy isolation devices is the next step. Each isolation point is then secured with a lock and tag, preventing any attempts to re-energize the equipment.
5. Verification
After the locks and tags are in place, a crucial verification step follows. This involves attempting to start the equipment to confirm that it remains inoperable. Voltage testers may be used for electrical equipment to ensure there is no residual electrical energy.
6. Performing Maintenance
With the equipment safely isolated and verified, maintenance or servicing activities can commence. Workers can perform their tasks without the risk of unexpected energization, ensuring a safe working environment.
7. Equipment Restoration
Once the maintenance work is complete, the equipment is restored to its normal operating condition. This involves removing the locks and tags, re-energizing the equipment, and ensuring that it operates as intended.
8. Communication
Throughout the entire process, clear communication is essential. Workers involved in the lockout must communicate effectively to ensure a smooth and safe transition from the lock out state to the restoration of normal operations.
Challenges
Implementing Lockout Tagout procedures can present challenges, including
- inadequate training
- lack of standardized procedures
- resistance to change within the organizational culture.
Overcoming these challenges requires a commitment to safety, ongoing training, and effective communication.
Best Practices
To ensure the success of Lockout Tagout programs, organizations should adopt several best practices:
- Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training to all employees involved in or affected by the Lock out Tag out procedure. This includes training on identifying energy sources, using locks and tags, and understanding the importance of the LOTO process.
- Clear Procedures: Develop clear and standardized Lock out Tag out procedures for each piece of equipment. These procedures should be easily accessible and regularly updated to reflect changes in equipment or processes.
- Regular Audits and Inspections: Conduct regular audits and inspections to ensure that Lock out Tag out procedures are being followed correctly. This helps identify areas for improvement and ensures ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
In the realm of industrial safety, the Lockout Tagout procedure stands as a sentinel, guarding against the potential hazards that lurk within the machinery and equipment. Its multifaceted purpose, encompassing worker safety, accident prevention, legal compliance, equipment integrity, operational efficiency, risk management, and worker empowerment, makes it an indispensable tool for organizations committed to fostering a safe and secure working environment. As industries evolve, the importance of mastering the Lockout Tagout procedure remains unwavering, reminding us that in the pursuit of progress, the safety of those propelling it forward should always come first.