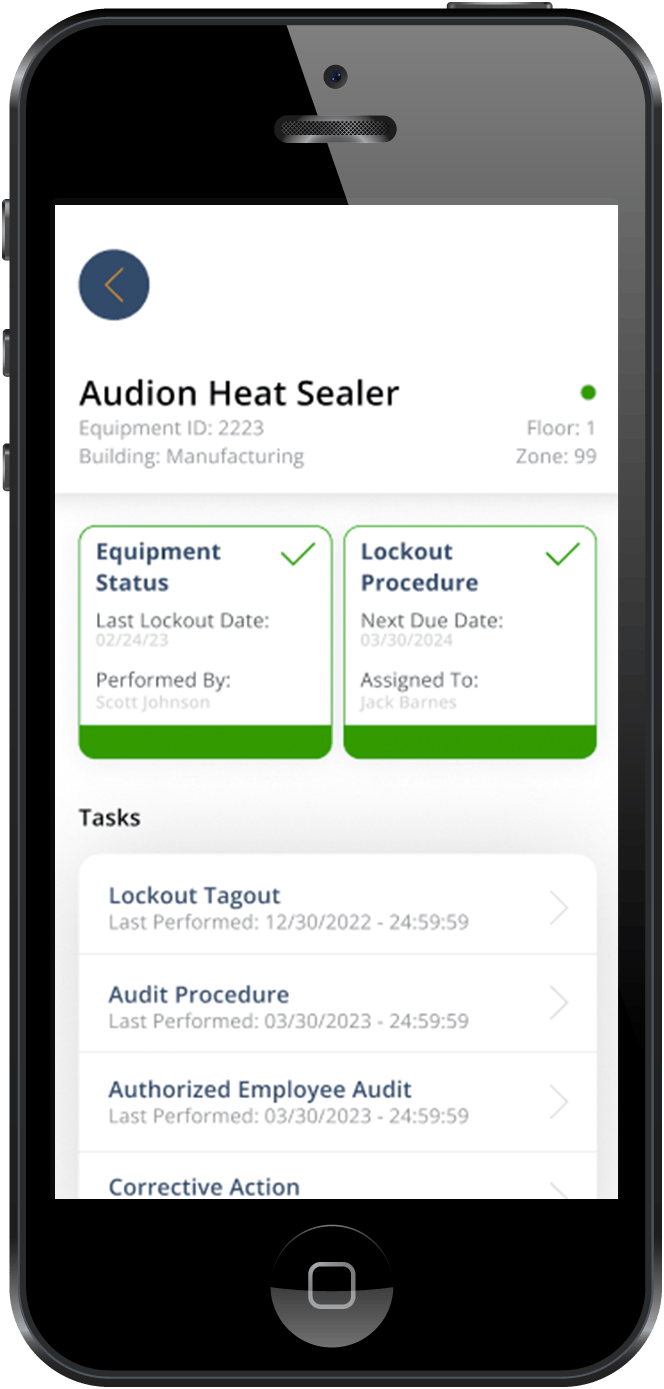
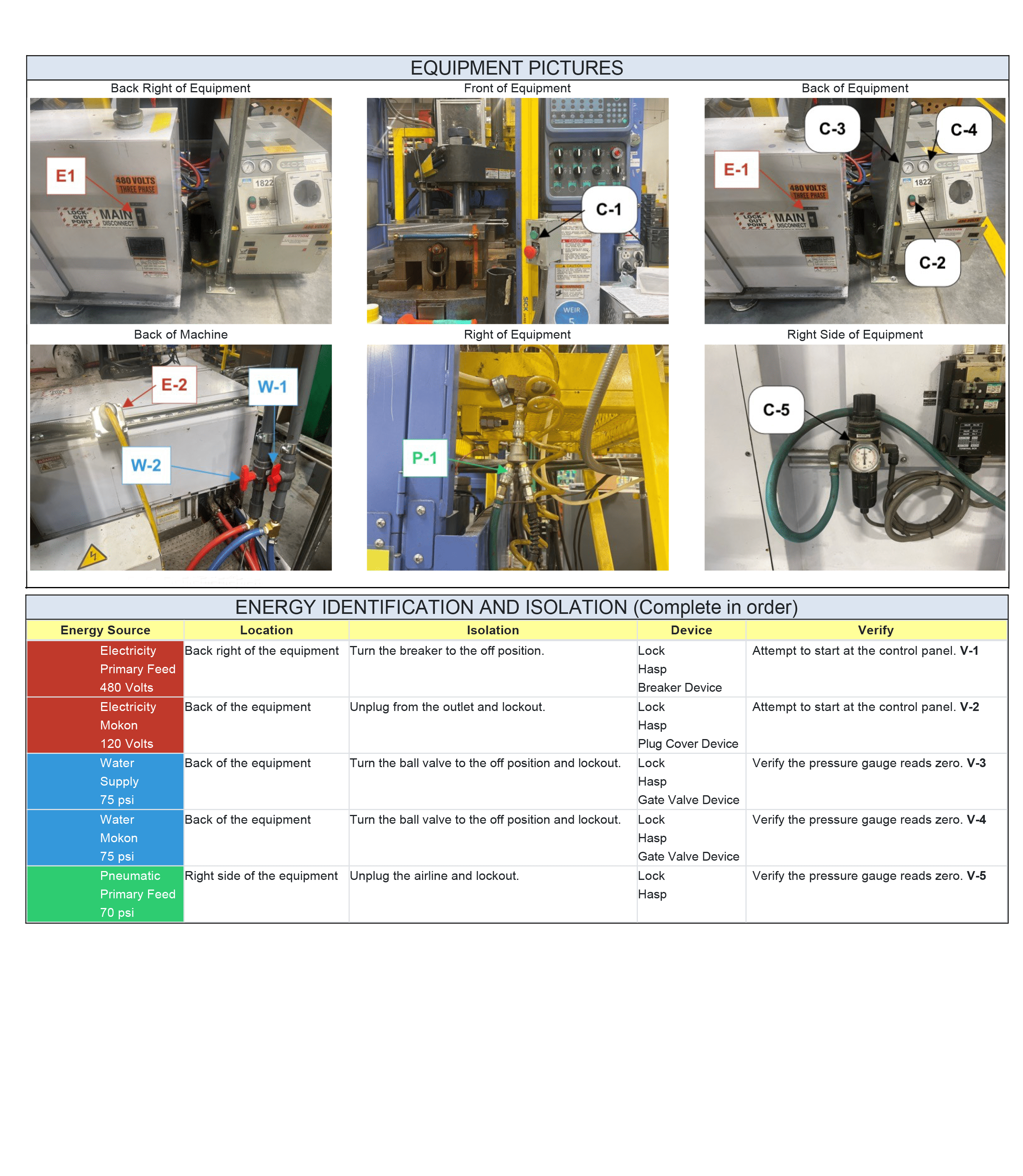
This article offers simple answers to many of the most frequently asked questions about lockout tagout. It aims to provide the basics of LOTO.

Lockout Tagout – Frequently Asked Questions (1)
Common Questions about Lockout Tagout
What is Meant By “Lockout Tagout”?
Lockout tagout is a safety program used in various industries to ensure that machines are properly shut down during maintenance or servicing work. The purpose of lockout tagout is to control hazardous energy and prevent accidental startup of machinery or equipment, which could lead to serious injuries or fatalities.
What is the Difference Between “Lockout” and “Tagout”?
The term “lockout” refers to the process of isolating a hazardous energy source and using a physical lock to secure it, while “tagout” involves attaching a warning tag to indicate that the equipment must not be operated. This dual approach creates a visible and tangible barrier to potential dangers, providing a layer of protection for those working on or around the equipment.
What is the OSHA Lockout Tagout Rule?
OSHA Lockout Tagout Standard: 29 CFR 1910.147 The Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout)
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a governing body in the United States responsible for releasing safety regulations including the standard 29 CFR 1910.147 The Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout). This Lockout Tagout regulation details the responsibility of employers to protect their workers from hazardous energy sources, machines, and equipment during servicing and maintenance activities. The standard covers topics such as what lockout and tagout are, when lockout tagout procedures should be performed, and how procedures should be conducted.
For a more in-depth overview of the lockout tagout rule, see our article here about OSHA 1910.147.
When Should Lockout Tagout Be Used?
Lockout/Tagout should be used any time there is the possibility of unexpected energization, start up, or release of hazardous energy of machines or equipment that could cause injury and harm to workers. This could apply to workers performing repairs, set up, servicing, inspections, cleaning, and other activities.
Because of its role in safety, lockout tagout procedures are often implemented in industries that deal with any form of hazardous energy (such as electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, thermal, and other energy sources).
What is a LOTO Procedure?
A Lockout Tagout procedure, often abbreviated as LOTO, is a safety procedure employed in industrial settings to ensure the complete isolation of energy sources from machinery or equipment during maintenance, repair, or servicing activities. The goal is simple yet profound – to prevent accidental energization or startup of machinery, which could pose serious risks to the safety of personnel involved.
What is the Correct Procedure for Lockout Tagout?
Lockout Tagout Procedures generally follow this sequence of events:
- Prep for Shutdown
- Notify Affected Employees
- Equipment Shutdown
- Isolation of Energy Sources
- Lockout Tagout Device Application
- Dissipation of Residual or Stored Energy
- Verification of Isolation
- Performing Maintenance or Servicing
- Release from Lockout Tagout
- Equipment Restart
- Documentation and Recordkeeping
However, keep in mind that LOTO procedures should be specified to a specific piece of machinery or equipment. This means that there may be additional steps or requirements based on individual circumstances.
What Should You Do if An Employee Is Not Available to Remove the Lock?
In the event that the authorized employee who applied the lockout/tagout device is unable to remove it, other workers should turn to direction from their manager or employer. This individual can ensure that correct procedures are followed and adequate communication is given so that another trained personnel can assist in removing the loto device(s).
Before taking any action, employers should do these 3 things:
- Ensure that the employee who applied the lock/tag is no longer at the facility
- Make a reasonable effort to notify the employee that their lock/tag is being removed by someone else
- Verify that the employee knows and understands that their device has been removed
For more guidance on this matter, see OSHA’s statements in 29 CFR 1910.147 (e)(3).
Who Enforces Lockout Tagout Requirements
Within the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), is the governing body responsible for enforcing lockout tagout requirements according to their established standard in 29 CFR 1910.147 The Control of Hazardous Energy.
Because OSHA is a government agency, they have legal authority pertaining to compliance with their safety standards. Those who are found noncompliant may receive violations and fines, according to the severity of their infringement.
Read more about OSHA violations and their associated consequences in this article here.
What is a LOTO Violation?
Companies that are found in violation of OSHA 1910.147 may incur a lockout tagout (LOTO) violation and associated fines. The value of these fines depends on the severity of the infraction. The different kinds of OSHA violations include:
- Other Than Serious Violation
- violations that are related to health and safety but that are very unlikely to result in a fatality or severe physical harm to an individual
- Serious Violation
- An infringement that could result in a high chance of death or severe physical harm to a person
- Willful Violation
- Violations in which the employer was knowingly and intentionally involved
- Failure to Abate
- Violation given to companies that procrastinate correction. (receive a re-inspection and have not fixed a previously-cited violation)
- Repeat Violation
- violations given to employers who have been cited for violating a rule, standard, or regulation are found committing a very similar violation upon re-inspection
Each of these kinds of violations have their own ranges for fines. Read more about the specifics of each kind of violation and the values of their associated fines here.
To avoid these violations and fines, it is helpful to be familiar with the mistakes employers and their companies make. Some of the most common LOTO-related violations include not having equipment-specific procedures, improper lockout tagout training, failure to conduct periodic inspections, and more.
To learn about the top 10 most common lockout tagout violations and how you can avoid them, read our article.
Why Are LOTO Locks Different Colors
While there isn’t any OSHA-mandated color system for lockout tagout, the OSHA recommended system for colored LOTO tags is as follows:
- Red Tags: Danger – Do Not Operate
- Yellow Tags: Caution – Out of Service
- Orange Tags: Warning – Information Only
- Fluorescent Orange/Orange-Red Tags: Biological Hazard – Beware
What are the Advantages of Using Software in Lockout Tagout?
There are many reasons that organizations choose to incorporate inspection software into their lockout tagout programs. Some of the advantages to using software, such as Smart Safety Pro technology, include:
- Customizable procedure building
- Paper-free documentation
- Detailed audit history
- Wifi is not required for use
- Organized information stats
- On-the-go reporting
To learn more about how Smart Safety Pro software could aid you in performing lockout tagout, request a demo!
Conclusion
Understanding lockout tagout is a crucial aspect of maintaining workplace safety. To help establish the basics of LOTO, this article outlines many of the most commonly asked questions about lockout tagout. It delves into topics such as what lockout and tagout are, how procedures are performed, and the reasons a company might receive a violation. For more in-depth information about LOTO, read the articles below!