Effective Lockout Tagout (LOTO) procedures are critical for ensuring the safety of employees who work with or around hazardous machinery and equipment. Not only that, but writing clear, detailed, and actionable LOTO procedures can help to prevent accidents, injuries, and costly downtime. Additionally, it can improve safety, compliance, and efficiency in the workplace. Because of this, it is worthwhile to develop quality procedures. This article dives into the key elements of LOTO and tips for writing better lockout tagout procedures.
What is a Lockout/Tagout Procedure?
A lockout tagout procedure is a set of equipment-specific safety steps that should be followed in order to safely shut down, de-energize, and secure machinery with hazardous energy. The purpose of lockout tagout procedures is to provide a framework for controlling hazardous energy and preventing accidental startup of machinery or equipment, which could lead to serious injuries or fatalities.

Smart Safety Pro Lockout Tagout Procedures on the Machine
Key Elements of Lockout Tagout Procedures
When writing lockout tagout procedures, it is essential to include all of the information that will be needed during the LOTO process. Often, lockout tagout procedures are broken up into sections of information that the reader can digest and implement as they go through the stages of shutting down and securing the equipment.
Here are the key elements that should be included in any and all lockout tagout procedures and what information they should provide.
Lockout Tagout Procedure Elements
- Scope, Purpose, and Authorization
This section defines the range and objective of the LOTO procedure and specifies who is authorized to perform and oversee the lockout process. Specifying authorization and the type of lockout ensures that only trained and competent individuals perform and oversee LOTO procedures. This reduces the risk of errors and enhances accountability.
- Lockout / Tagout Application Steps
The lockout / tagout application process portion of procedures provides a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to safely apply lockout and tagout devices to isolate hazardous energy sources. Clear instructions minimize the risk of errors, ensuring that all necessary steps are completed in the correct order, thus preventing accidental energization.
Detailed steps ensure that every worker follows the same procedure, maintaining consistency and compliance with safety regulations. Each step included in this section is designed to systematically eliminate potential hazards, ensuring that all energy sources are properly isolated before maintenance begins.
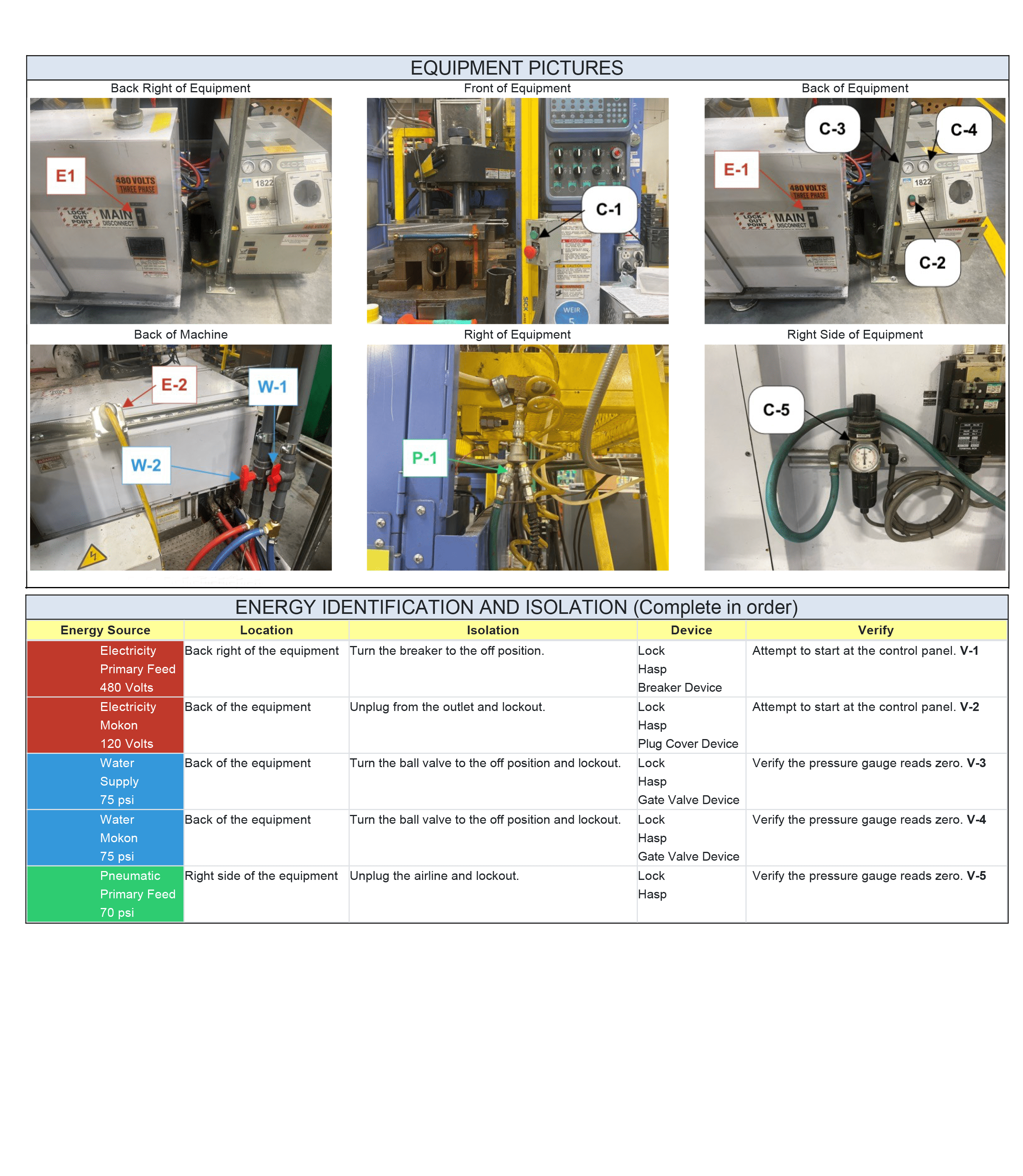
- Equipment Pictures
Visual aids, such as pictures of the equipment and energy isolation points, are included in the procedure. These can help the authorized worker(s) quickly identify the correct equipment and isolation points, reducing the chance of mistakes.
The purpose of visual aids is to complement written instructions, making it easier for workers to understand and follow the procedure. They can also be valuable for training new employees by helping them become familiar with the machinery and its components.
- Energy Identification and Isolation
This section identifies the energy source type, details where it is found, and gives direction for isolating the energy source and verifying it has been correctly shut off.
The “Energy Identification and Isolation” section provides crucial information to the worker by identifying all necessary hazardous energy sources and how to safely prevent accidental release of energy. This way, workers can create a safe environment to work in, protecting themselves and others from unexpected energization.
- Return to Service Steps / Lock and Tag Removal Process
This section outlines the steps for 2 key processes: safely removing lockout tagout devices and returning the equipment to normal operation.
The instructions outlined in this section should clearly indicate important steps such as verification that maintenance is complete, notifying affected employees before removing LOTO devices, and how to correctly re-energize the machinery. By providing simple guidance for removing lockout devices and returning equipment to service, companies help ensure that the machinery is safely transitioned back to operational status without risking worker safety.
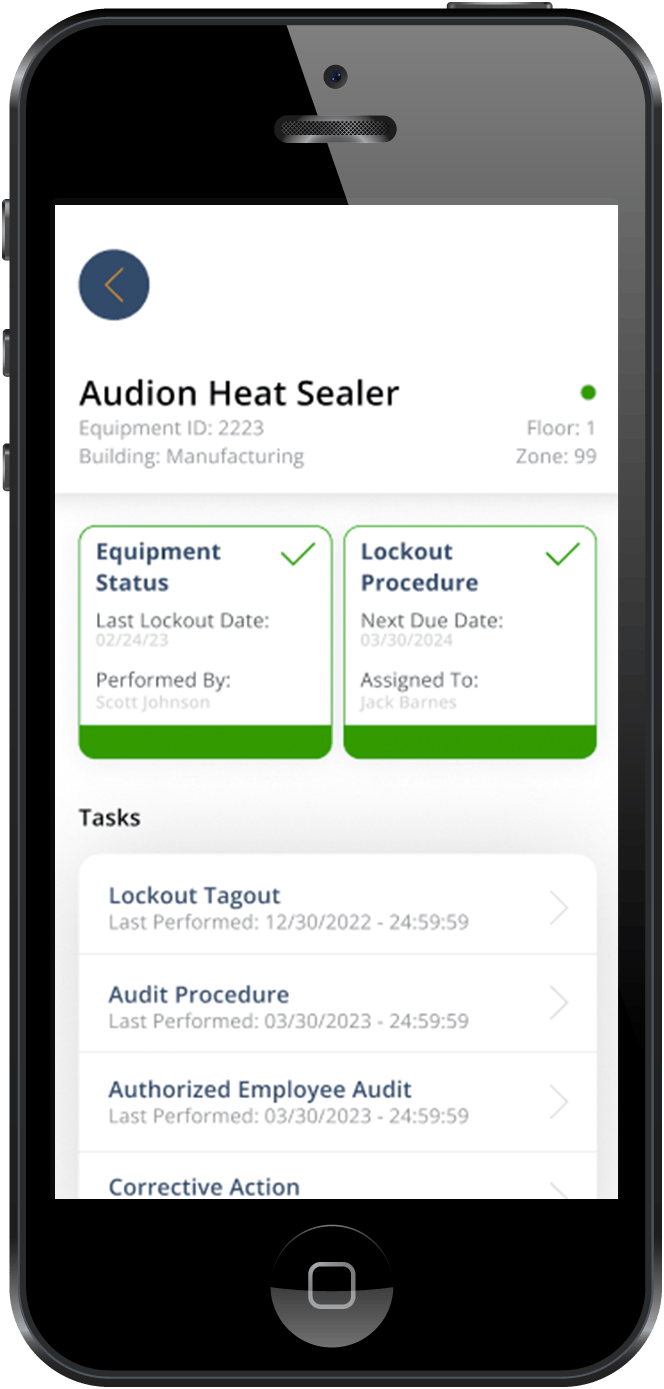
**Note: Some lockout tagout procedures also include a QR code that can be scanned and used alongside software to record loto steps as they are performed.
Each element of written lockout tagout procedures plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of workers and effectiveness of the LOTO process.
What does OSHA say about LOTO Procedures?
OSHA 1910.147 The Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout) is a safety standard that has been established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration outlining what companies and organizations need to know to maintain compliance for lockout tagout. This standard clearly states that employers are required to “establish a program and utilize procedures for affixing appropriate lockout devices or tagout devices to energy isolating devices, and to otherwise disable machines or equipment to prevent unexpected energization, start-up or release of stored energy in order to prevent injury to employees.”
The standard goes into further depth on procedures by stating that procedures should be “developed, documented and utilized for the control of potentially hazardous energy when employees are engaged in the activities covered by this section” (lockout tagout).
There is an exception to this rule, however, it comes with a number of specific criteria.
Exception as stated by OSHA: “The employer need not document the required procedure for a particular machine or equipment, when all of the following elements exist:
(1) The machine or equipment has no potential for stored or residual energy or reaccumulation of stored energy after shut down which could endanger employees;
(2) the machine or equipment has a single energy source which can be readily identified and isolated;
(3) the isolation and locking out of that energy source will completely deenergize and deactivate the machine or equipment;
(4) the machine or equipment is isolated from that energy source and locked out during servicing or maintenance;
(5) a single lockout device will achieve a locked-out condition;
(6) the lockout device is under the exclusive control of the authorized employee performing the servicing or maintenance;
(7) the servicing or maintenance does not create hazards for other employees; and
(8) the employer, in utilizing this exception, has had no accidents involving the unexpected activation or re-energization of the machine or equipment during servicing or maintenance.”
For any situations involving lockout tagout that do not meet all 8 stipulations above, the following guidance from (1910.147(c)(4)(ii) should be adhered to for the writing and usage of lockout tagout procedures.
Section (1910.147(c)(4)(ii) specifies that procedures should outline the scope, purpose, authorization, rules, and techniques for controlling that source of hazardous energy.
In order to write compliant lockout tagout procedures, the procedures should at least include the following information:
- A statement specifying the intended use of the procedure
- Procedural steps for the shut down, isolation, blocking and security of machines or equipment to control hazardous energy;
- Detailed procedural steps for the placement, removal and transfer of lockout devices and tagout devices and the responsibility for them; and
- Requirements for testing a machine/equipment to verify the effectiveness of lockout devices, tagout devices, and other energy control measures.

Writing Lockout Tagout Procedures
Pointers for Improving Procedures
When it comes to improving procedures, one of the best practices is to write with the end user in mind.
After all, lockout tagout procedures should be written so that any authorized employee can properly perform their duties. Procedures are meant to equip users with adequate knowledge and information to safely perform their responsibilities with confidence. The following tips are all ways that the procedure author can write lockout tagout procedures with the worker(s) that will use them in mind.
1. Be Familiar With the LOTO Process
- Tip: Become acquainted with the process that workers undergo when actually performing lockout tagout procedures.
- Why it Matters: Familiarity with the process will help with organizing the necessary information in a way that flows for the worker.
- Typically, lockout tagout procedures look a little something like this:
- 1. Prep for Shutdown & Notify Affected Employees
- 2. Equipment Shutdown
- 3. Isolation of Energy Sources
- 4. Lockout Tagout Device Application
- 5. Dissipation of Residual or Stored Energy
- 6. Verification of Isolation
- 7. Performing Maintenance or Servicing
- 8. Release from Lockout Tagout
- 9. Equipment Restart
- 10. Documentation and Recordkeeping
- Typically, lockout tagout procedures look a little something like this:
- Best Practice: Learn about the 10 steps of lockout tagout and discuss them with workers to ensure that written lockout tagout procedures are logical and helpful.
2. Understand Your Equipment and Energy Sources
- Tip: Start by thoroughly understanding the machinery and equipment your procedures will cover. This includes identifying all energy sources—electrical, hydraulic, pneumatic, mechanical, chemical, and thermal—and the methods required to isolate them.
- Why It Matters: Different types of equipment have unique energy sources and control points, which need to be isolated during maintenance. Without this foundational knowledge, LOTO procedures may miss critical energy sources, putting workers at risk of injury.
- Best Practice: Create a detailed equipment inventory and document the specific energy sources for each machine. This ensures your procedures are tailored to the exact equipment and energy hazards in your facility.
3. Write Procedures in Simple, Clear Language
- Tip: Use clear, simple, and concise language when writing LOTO procedures. Avoid technical jargon that could confuse workers, especially those who are not engineers or technical experts.
- Why It Matters: LOTO procedures are typically used by workers under time constraints or stress. Overly complex language can lead to misunderstandings or incorrect implementation of procedures, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Best Practice: Break down each step in the procedure into clear, actionable instructions. Use bullet points or numbered lists to make the process easy to follow
4. Use Visual Aids and Diagrams
- Tip: Incorporate visuals such as diagrams, photos, and flowcharts into your LOTO procedures to help clarify complex steps.
- Why It Matters: Workers may better understand how to isolate energy sources or lock out machinery when they can see clear visuals. Diagrams showing the location of switches, valves, or lockout points can reduce confusion and ensure accuracy.
- Best Practice: Include labeled diagrams or photographs of the actual machinery, highlighting the key components that must be locked out. This can be especially helpful for large or complex equipment where key control points might not be immediately obvious.
5. Customize Lockout Tagout Procedures for Each Machine
- Tip: Ensure that each piece of equipment has a unique, equipment-specific LOTO procedure. Avoid using generic templates for all machinery, as different equipment requires different steps to control hazardous energy.
- Why It Matters: A one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work when dealing with the varied types of machinery in a facility. A procedure that works for one machine might not apply to another, leading to unsafe practices or missed steps.
- Best Practice: Tailor LOTO procedures to each machine by documenting the exact steps needed to safely shut down, isolate energy, and verify de-energization for that specific piece of equipment.
6. Clearly Define Roles and Responsibilities
- Tip: Identify and define who is responsible for each step of the LOTO process, including the roles of authorized employees, affected employees, and supervisors.
- Why It Matters: Defining roles ensures that everyone involved knows their specific responsibilities, reducing confusion and the potential for errors. Authorized employees need to know exactly what actions to take, while affected employees need to understand when and why equipment is locked out.
- Best Practice: Include a section in each LOTO procedure that outlines the roles of all involved parties, specifying who is authorized to apply and remove locks and who should be notified.
7. Focus on Sequence and Verification Steps
- Tip: Carefully outline the exact sequence of steps that need to be followed when locking out equipment, and emphasize the importance of verification after applying locks.
- Why It Matters: Following the correct sequence of actions ensures that all energy sources are effectively isolated. Verification is crucial for confirming that energy has been properly controlled before work begins, ensuring no hazardous energy remains.
- Best Practice: Provide a step-by-step process that starts with shutting down equipment, followed by isolation and lockout of each energy source, and ends with verification to ensure that equipment cannot be accidentally restarted.
8. Account for Group Lockout Situations
- Tip: If your facility has equipment that requires multiple workers to perform maintenance, be sure to incorporate group lockout procedures that account for multiple locks and personnel.
- Why It Matters: Group lockout ensures that each worker involved in the maintenance process applies their own lock, preventing accidents by ensuring that the machine cannot be re-energized until all workers have completed their tasks.
- Best Practice: Develop clear group lockout procedures that specify how locks will be applied, managed, and removed. Use a lockbox system if necessary to manage group lockout situations effectively.
9. Address Shift Changes and Personnel Transitions
- Tip: Include procedures for managing shift changes or personnel transitions during a LOTO process, ensuring continuity in lockout control between shifts.
- Why It Matters: Equipment may remain locked out across multiple shifts, and without clear procedures, there is a risk of unauthorized removal of locks or incomplete lockout transfers. This can result in dangerous situations if workers assume machinery is safe when it isn’t.
- Best Practice: Develop a formal process for transferring lockout control, ensuring that incoming personnel verify the lockout status and understand the work in progress.
10. Regularly Review and Update Procedures
- Tip: Make it a priority to periodically review and update LOTO procedures to ensure they remain accurate and up to date with current equipment and regulations.
- Why It Matters: Machinery and work processes change over time, and regulations may be updated. Outdated procedures can lead to safety lapses or non-compliance with industry standards.
- Best Practice: Schedule annual reviews of all LOTO procedures and make necessary updates as equipment or operational changes occur. Keep an audit trail of any revisions made.
11. Conduct Regular Training and Retraining
- Tip: Ensure all employees are properly trained in the LOTO procedures and receive periodic retraining to reinforce their knowledge.
- Why It Matters: Even well-written procedures won’t be effective if workers don’t understand them or fail to follow them. Ongoing training ensures that employees stay aware of the procedures and are comfortable implementing them correctly.
- Best Practice: Provide comprehensive training sessions for all employees who are involved in LOTO, and conduct regular refresher courses to keep everyone up to date. Incorporate hands-on training whenever possible to reinforce proper procedure execution.
12. Incorporate Software
- Tip: Where possible, use updated technology and equipment to write, perform, and document lockout tagout procedures.
- Why it Matters: Technology can offer a variety of benefits for LOTO programs including help with writing procedures, a centralized place for storing data, and more accurate record keeping.
- Best Practice: Invest in and incorporate software that can aid in managing the LOTO program. Train users on how to best use the software. Additionally, review documents to recognize trends, areas of improvement, and other valuable insights.
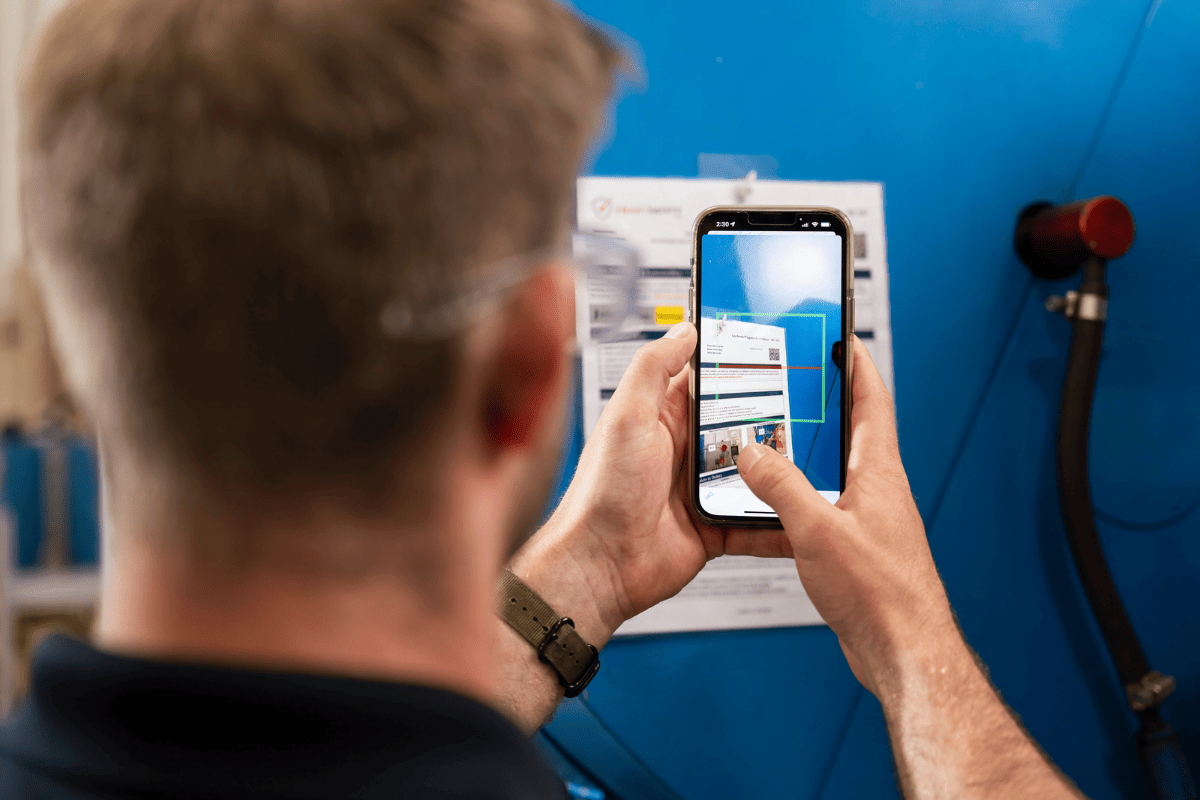

Using Software to Perform Lockout Tagout
How Our Software Can Help With Lockout Tagout
There are a multitude of reasons why more and more companies are making the switch to use lockout tagout software in their LOTO programs. These are some of the advantages of using software to write lockout tagout procedures and run a LOTO program.
Streamlined Processes: Software solutions can automate various aspects of the LOTO process, such as tracking the status of lockouts and notifying relevant personnel of updates or changes. Through these software features, lockout tagout is organized and simplified.
Improved Efficiency & Time Savings: With our software, lockout tagout procedures can be created in MINUTES! These immense time savings can then be converted into more time for managing other assets and processes. Faster access to information and automated workflows help reduce the time required to implement and release lockouts, minimizing equipment downtime and increasing productivity.
Elimination of Human Error: Using software systems can ensure that the correct procedures are followed by linking the correct lockout tagout steps to their associated equipment. This reduces the risk of human error, which is a common cause of accidents in LOTO processes. Not only this, but the step-by-step verification helps with maintaining compliance by requiring specific actions to be completed before moving on to the next step, ensuring that no critical steps are overlooked.
Automated Documentation: Software solutions automatically log all LOTO activities, creating a comprehensive digital record. This documentation includes details such as who performed the lockout, when it was done, and any issues encountered. These digital records are easily accessible for audits and inspections, helping organizations demonstrate compliance with safety regulations and standards.
Real-Time Updates: QR codes and software systems can provide real-time updates on the status of lockout procedures. Workers and supervisors can instantly see which equipment is locked out, who is responsible, and when it is expected to be released. This results in readily available data and improved communication among team members.
Enhanced Collaboration: Digital platforms facilitate better communication and coordination among team members, especially during complex or group lockout situations. Multiple users can access and update information simultaneously, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Detailed Audit Trails: Every action taken during the LOTO process is recorded in the software system, creating a detailed audit trail. This traceability helps in investigating incidents, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring accountability. Since QR codes link directly to specific equipment and procedures, there is clear documentation of who performed the lockout and when, enhancing individual accountability.
Scalable Solutions: QR codes and software systems can be easily scaled to accommodate growing operations. Adding new equipment or updating procedures can be done quickly and efficiently within the digital platform. This scalability makes these solutions suitable for organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises.
Adaptability to Changing Regulations: As safety regulations evolve, software solutions can be updated to reflect new requirements. This ensures that LOTO procedures remain compliant with the latest standards without the need for extensive manual revisions. QR codes can be reprogrammed to link to updated procedures, ensuring that workers always have access to the most current information.
Try It For Yourself
As time goes on, more and more companies are making the switch and integrating software capabilities into their lockout tagout programs. With benefits such as paperless documentation and real-time updates, integrating software is a no-brainer for a lot of organizations. However, it makes sense to be hesitant or want to learn what you can before diving in.
At Smart Safety Pro, we don’t want you to just choose our software, but we want you to love your choice. To help you decide whether or not our program works for your situation, we offer free demos.
With a free demo, you can set up a time to meet with one of our professionals and talk about your organizational needs. This way, you can gather information and make an informed decision about what’s right for your company’s future.
Click here to learn more about how Smart Safety Pro can enhance your lockout tagout program.
Conclusion
Writing effective Lockout Tagout procedures is a critical step in ensuring workplace safety and compliance with regulatory standards. By tailoring procedures to each piece of equipment, using clear language, incorporating visual aids, and regularly reviewing and updating your procedures, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and enhance the overall safety culture in your facility. Additionally, software can be a significant tool for increasing efficiency and accuracy when writing lockout tagout procedures, training on them, and performing them. Implementing these tips will lead to more efficient, understandable, and reliable LOTO procedures that keep both employees and equipment safe.